Use this Stair Calculator to precisely calculate step dimensions for any staircase project. Enter your total rise, run, and desired step count, and the tool will provide accurate tread depth, riser height, stringer length, and slope angles, ensuring your staircase meets safety and building code requirements.
Perfect for students, engineers, quantity surveyor, builders, contractors, architects, and DIY enthusiasts, this calculator simplifies staircase planning, reduces errors, and saves time on design and construction. Get instant, reliable results for straight, L-shaped, or custom staircases — no registration or downloads required.

Challenge your understanding of stair design principles, building codes, and construction techniques with our 10-question professional assessment.
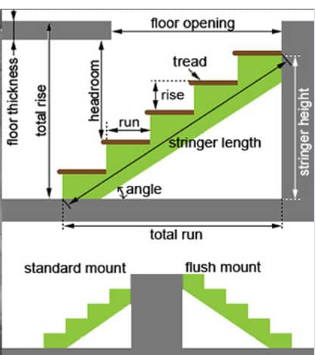
Vertical distance between floor levels. Measure from finished floor to finished floor.
Horizontal depth of each step. Minimum 10" required by most building codes.
Vertical height between steps. Maximum 7.75" per International Residential Code.
Minimum 6'8" vertical space above any step. Critical for safety compliance.
Understanding proper terminology ensures accurate communication with contractors and inspectors:
| Term | Definition | Standard Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Riser | Vertical face between treads | 6.5" - 7.75" |
| Tread | Horizontal walking surface | 10" minimum |
| Nosing | Tread overhang beyond riser | 0.75" - 1.25" |
| Stringer | Diagonal support structure | Varies by design |
| Going | Horizontal distance between risers | Equal to tread depth |
| Parameter | Residential Code | Commercial Code |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Riser Height | 7.75 inches | 7.0 inches |
| Minimum Tread Depth | 10.0 inches | 11.0 inches |
| Minimum Headroom | 6 feet 8 inches | 6 feet 8 inches |
| Handrail Height | 34-38 inches | 34-38 inches |
| Minimum Width | 36.0 inches | 44.0 inches |
Proper stair design blends architectural aesthetics with ergonomic functionality and strict safety compliance. The relationship between rise and run determines not only comfort but also accessibility and code adherence. Professional builders utilize mathematical formulas to ensure optimal stair performance.
The industry standard for comfortable stair design follows this mathematical relationship: 2R + G = 25 inches, where R represents riser height and G represents going (tread depth). This formula, developed through decades of ergonomic research, creates stairs that accommodate natural human stride patterns while minimizing fatigue.
Stair pitch, measured in degrees, significantly impacts user experience. The optimal range of 30° to 37° balances space efficiency with comfort. Calculate pitch using: Pitch = arctan(Riser ÷ Tread). Steeper pitches above 40° become difficult for children and elderly users, while shallower pitches below 30° consume excessive floor space.
Different materials require specific calculation adjustments:
Account for wood shrinkage (approximately 3-5%) and grain direction. Pressure-treated lumber requires additional drying time calculations.
Include weld shrinkage allowances and expansion joint calculations for temperature variations in metal staircases.
Factor in concrete slump, curing shrinkage, and formwork deflection. Allow for 1/8" per foot camber in long spans.
For complex stair designs, additional calculations become necessary:
Always measure from structural surfaces, not finished floors, during framing. Account for future flooring materials by creating detailed elevation plans before construction begins.
Verify all riser heights within 1/8-inch tolerance. Use laser levels for accuracy. Inconsistent risers create tripping hazards and violate building codes.
Wood expands and contracts with humidity changes. Allow for 1/16-inch gaps between treads in humid climates. Use acclimated materials to minimize seasonal movement.
Verify: 4-inch sphere rule (no openings larger than 4 inches), continuous handrails, adequate lighting, non-slip surfaces, and proper nosing visibility.
Explore our comprehensive suite of professional calculation tools designed for construction, engineering, and home improvement projects:
Compute material requirements for earthwork, concrete, and structural elements with precision.
Determine exact concrete volumes for slabs, footings, columns, and other structural components.
Calculate heating and cooling requirements for residential and commercial spaces accurately.
Estimate tile quantities, grout requirements, and material costs for flooring and wall projects.
Compute shingle requirements, underlayment needs, and roofing material costs for any roof pitch.
Determine mulch volume requirements for garden beds, landscaping projects, and yard maintenance.
Calculate gravel, crushed stone, and aggregate quantities for driveways, pathways, and drainage.
Estimate paint gallons, primer needs, and coverage for interior and exterior painting projects.
Calculate Body Mass Index and evaluate health metrics based on height and weight measurements.